Table of Contents
Biometrics
In their technical meaning, biometrics are body measurements and calculation relating to human characteristics. The resulting identifiers are distinctives, measurable characteristics that can be used to label and describe individuals. They can be categorized as physiological or behavioral.
Biometric data have various applications, for example in law enforcement, healthcare, civil identity & voters registrations.
Biometric authentication
The process of verifying your identity to access a service, app or device, is known by definition as biometric authentication.
How biometric authentication works
Basically, biometric authentication works by comparing two sets of data. The first set is initially created by the account or device owner, while the second is entered by the visitor. If both sets are nearly identical, the visitor and the owner are confirmed as being the same individual, and access is granted.
Since an identical match is almost impossible, the biometric data sets are only required to be nearly identical. This diminishes the chances of a false negative. However, it also augments the chances of a wrongful positive match.
Biometric authentication methods
Fingerprint scanners
Fingerprint scanners can either rely on optical, capacitive or ultrasound technology.
Google and Apple both store encrypted fingerprint data on devices themselves without making a copy on their own servers. Will it can be hacked, fingerprint is still an extremely safe biometric authentication method.
Smartphone under screen sensor
In recent years, smartphone companies have increasingly launch all-screen designed phone, removing the home button from their models. Getting rid of it also meant that the fingerprint reader had to be placed somewhere else. Most companies moved it to either to the back of the device or to a button on the side of the device. However, new technology is allowing developers to install the fingerprint sensor directly under the screen, where the users intuitively touches the screen to wake the phone. In-screen fingerprint sensor are predicted to become the new standard.
Eye scanners
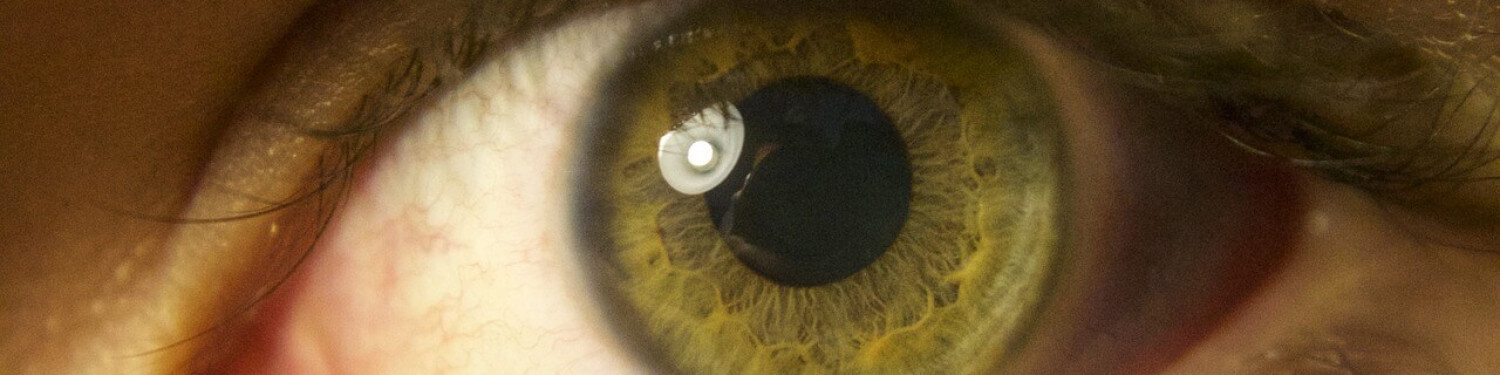
Eyes are considered to be one of the most reliable body parts for biometric authentication, as the retina and iris remains mostly unchanged throughout a person’s lifetime. Retinal patterns and irises are, much like fingerprints, unique to each individual.
Retinal scans illuminate, with infrared light, the complex blood vessels in the eye, making them more visible than the surrounding tissue. Iris scanners compare high-quality photos or videos of one or both irises.
Iris scanner have been proved to be vulnerable to false positive with high-quality pictures.
Speaker recognition
Unlike voice recognition, speaker recognition identifies who is speaking, rather than what is being said.
To do so, specialized software break down words into formants, or packets of frequencies. These form a voice print, notably through the voice tone. Speaker recognition technology can either be text-dependent, i.e. granting access after identifying certain words or phrases, or text-independent, meaning it attempt to recognize the voice regardless while ignoring what is being said.
Speaker recognition is particularly vulnerable, as obtaining a high-quality recording of someone’s voice is quite easy. Furthermore, background noises may distort the person’s voice and cause a false negative.
Facial recognition systems
Classic methods to identify someone’s identity using their facial features look at eyes, nose, the distance between the lips and the nose. Other features like skin texture, beauty marks or wrinkles, can also be compared into a mathematical space. All of these can easily be fooled with makeup, masks or even by hiding some parts of the face. For this reason, facial recognition evolved to use more advanced technologies, including thermal imagery.
Apple Face ID was presented back in September 2017 as a major step in secure biometric authentication. Its process is more complex than classic face recognition methods. A dot projector, infrared camera and flood illuminator map and recognized the face looking at it. First, Face ID projects more than 30,000 invisible IR dots. The IR image and dot pattern created are process through the neural network to create a mathematical image of the user’s face. Machine learning capabilities should allow the iPhone to learn to recognize its owner face, adapting to changes in appearance over time and regardless of temporary changes. Meaning that wearing hats, scarves, glasses or changes in light should therefore not interfere with the recognition process.
While Apple claim there be only a one-in-a-million chance of someone else being able to unlock your phone, Face ID technology has shown some weaknesses. In some cases, kids could unlock their parent’s phone. Even Apple had some problem unlocking their product during demo. More worrisome, security specialists have also proved its hackability.
Hand and finger geometry
The shape of our hands, while not as unique as fingerprints, iris or tridimensional face maps, are different enough from one person to another to identify users with a low accuracy. Hand geometry scanner measure palm thickness, finger length and width, knuckle distance, among others.
Vein geometry
Our vein layout is completely unique. It even varies from one hand to another. A strong advantage of vein geometry recognition, is that veins patterns are incredibly difficult to copy and steal, as they are only visible under tightly controlled circumstances. Vein geometry scanners use near-infrared light to make the veins visible on picture.
Biometrics and security
A new study from Veridium has revealed that 86% of IT decision makers agree that biometrics is the most secure authentication method for both organizations and consumers to use.
In the end, the goal of biometric authentication is security. In that venture, it is always compared to password or PIN code.
Advantages and disadvantages of biometric authentication
The biggest advantage of biometrics is its usability. In most cases, the identification only takes a few seconds, and users do not need to remember a password.
The biggest weakness of biometrics is that registered data sets cannot be remotely altered or deleted. In other words, thief could steal a smartphone and use a fake finger to unlock it at will. However, one must keep in mind that hackers or thief also need to be in your physical proximity to collect biometric data needed to bypass login.
Researchers have proven that a set of 5 “master fingerprints” can unlock ca. 65% of devices. This can be example by the fact that smartphones fingerprint sensors are often small, and therefore relying on a partial match. In real life conditions, this open rate should go down to around 10-15%, which is a huge window, exposing millions of devices.
Biometrics last a lifetime. Password can be modified if there is a doubt that someone learned it, or on a regular basis, out of precautions. Once a working copy of your biometrics is out there, there is nothing to do, outside switching to password. In one of the biggest cybersecurity breach in history, the US Office of Personnel Management leaked 5.6 million employee fingerprints. For the government officials involved, a part of their identity will always be compromised. The permanence of breaches involving biometric data are particularly concerning to privacy experts, as the effects will be felt for years to come.
Finally, vulnerabilities in biometric authentication software might put your device at risk. For example, a couple years ago, security researchers were able to exploit weaknesses in Android devices to remotely extract user’s fingerprints and use backdoors to hijack mobile payment or even install malware. While patches have addressed those specific vulnerabilities, bug hunters and hackers are always on the hunt for new flaws.
How to secure your device’s fingerprint readers
A few general recommendations can help make device safer. Fingerprint-resistant or oleophobic cover and screen protector will avoid leaving a clear fingerprint on the device. As most users register their index and thumb, using a different finger is recommended. However, the most secure alternative is to use both fingerprint and a password.
Behavioral biometrics and fraud
SecuredTouch, one of the digital fraud prevention pioneers, gained a leading role in the industry worldwide by focusing on mobile applications. The technological platform operated by the Israeli behavioral biometric firm creates unique user profiles, based on the interaction between users and end devices, authenticating consumers in the background, thus preventing misuse. Basing the profile on behavioral online shopping patterns offers consumers an efficient protection against identity theft or account takeovers, as those patterns can rarely be imitated. The technology detects fraudulent behavior and attempted fraud through automated computer attacks carried out using emulators, bots and malware.
Biometrics in payment
Nowadays, nearly all smartphones and tablets, as well as some laptops, have biometric sensors. These authentication methods replace the user’s password to unlock the device, but also on payment and banking apps or websites.
Some point-of-sale terminals also incorporate biometric sensors. Those are particularly useful in markets with low banking penetration. In Mexico, for example, biometrics could be used to verify the identity of loan applicants, an obligation Mexican banks face for all applicants.